دليل لأنظمة الذكاء الاصطناعي متعددة الوكلاء
إن موظف القروض المبتدئ الذي يتعامل مع إدخال البيانات وفحص المخاطر والقرارات النهائية وحده يكون عرضة للأخطاء لأن الدور يتطلب الكثير في وقت واحد. وتظهر نقطة الضعف نفسها في وكلاء الذكاء الاصطناعي المتجانسين الذين يُطلب منهم تشغيل عمليات سير عمل معقدة ومتعددة المراحل. إنهم يفقدون السياق، ويتخطون الخطوات، وينتجون تفكيرًا هشًا، مما يؤدي إلى نتائج غير موثوقة.
النهج الأقوى هو هيكلة الذكاء الاصطناعي كفريق خاضع للإشراف من المتخصصين الذين يفرضون النظام والمساءلة. ويعكس هذا التعاون بين الخبراء وينتج عنه قرارات أكثر اتساقًا وقابلية للتدقيق في المجالات عالية المخاطر مثل الإقراض. في هذه المقالة، قمنا ببناء مثل هذا النظام المنسق، ليس كعامل واحد مثقل بالعمل، ولكن كفريق منضبط.
ما هو الوكيل المشرف؟
الوكيل المشرف هو وكيل خاص لم يعد وكيلاً لأداء المهام، ولكنه بالأحرى منظم لفريق من الوكلاء الآخرين الذين يعملون في مهمة ما. اعتبره رئيسًا لقسم القوى العاملة في مجال الذكاء الاصطناعي لديك.
وتشمل مسؤولياتها الرئيسية ما يلي:
- تحليل المهام والتفويض: يأخذ المشرف الطلب الوارد ويقسم الطلب إلى مهام فرعية منطقية ثم يتم إرسالها بعد ذلك إلى الوكيل المتخصص المناسب.
- تنسيق سير العمل: إنه صارم في ترتيب العمليات. وفي حالة مراجعة القروض لدينا، فإن ذلك يعني استرجاع البيانات، ومراجعة السياسات، وبعد ذلك فقط يتم تقديم التوصية.
- ضبط الجودة: فهو يتحقق من أداء كل وكيل عامل لمعرفة ما إذا كان يصل إلى المعيار المطلوب قبل الخطوة التالية.
- تجميع النتيجة: بمجرد الانتهاء من جميع وكلاء العمال، يأخذ المشرف مخرجات العمال ويجمعها لإعطاء نتيجة نهائية متماسكة.
تكون نتيجة هذا النمط أكثر قوة وقابلية للتطوير وأسهل في تصحيح أخطاء الأنظمة. يتم تكليف الوكلاء بمهمة واحدة وهذا يبسط منطقهم ويزيد من استقرار أدائهم.
التدريب العملي: أتمتة مراجعات القروض مع المشرف
ويجري الآن إنشاء نظام المراجعة الأولى لأتمتة طلبات القروض. نحن نهدف إلى الحصول على هوية مقدم الطلب، وتقييمه فيما يتعلق بسياسات مخاطر الشركة، وتقديم المشورة بشأن الإجراء الدقيق الذي يجب اتخاذه.
سيتكون فريق الذكاء الاصطناعي لدينا من:
- عامل تناول الحالة: أخصائي مكتب الاستقبال. يقوم بجمع المعلومات المالية لمقدم الطلب ووضع ملخص.
- وكيل مدقق سياسة المخاطر: المحلل. يقوم بمطابقة معلومات مقدم الطلب مع سلسلة من معايير الإقراض المحددة مسبقًا.
- وكيل قرار الإقراض: صانع القرار. يأخذ الاكتشافات ويقترح مسار العمل النهائي مثل الموافقة على القرض أو رفضه.
- المشرف: المشرف الذي يقوم بسير العمل بأكمله ويضمن أن كل وكيل يقوم بشيء ما بالتسلسل الصحيح.
دعونا نبني هذا الفريق المالي.
الخطوة 1: تثبيت التبعيات
سيعتمد نظامنا على LangChain وLangGraph وOpenAI. LangGraph هي مكتبة تم تطويرها لإنشاء مسارات عمل متعددة الوكلاء.
!uv pip install langchain==1.2.4 langchain-openai langchain-community==0.4.1 langgraph==1.0.6 الخطوة 2: تكوين مفاتيح API والبيئة
قم بإعداد مفتاح OpenAI API الخاص بك لتشغيل نماذج اللغة لدينا. ستطالبك الخلية أدناه بإدخال مفتاحك بشكل آمن.
import os
import getpass
# OpenAI API Key (for chat & embeddings)
if not os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY"):
os.environ("OPENAI_API_KEY") = getpass.getpass(
"Enter your OpenAI API key (https://platform.openai.com/account/api-keys):\n"
)الخطوة 3: الواردات
سيتطلب تعريف الدولة والأدوات والوكلاء عدة عناصر من مكتباتنا.
from typing import Annotated, Literal
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langgraph.types import Command
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, SystemMessage, AIMessage
from langchain.agents import create_agent
from IPython.display import display, Markdownالخطوة 4: منطق الأعمال – مجموعات البيانات
سنقوم بتشغيل نظامنا على بيانات مجردة في الذاكرة والتي ستكون بمثابة تمثيل لسياسات المخاطر وتوصيات القروض وسجلات المتقدمين. وهذا يجعل مثالنا قائمًا بذاته وسهل المتابعة.
risk_policies = (
{
"loan_type": "Home Loan",
"risk_category": "Low Risk",
"required_conditions": (
"credit_score >= 750",
"stable_income >= 3 years",
"debt_to_income_ratio < 30%"
),
"notes": "Eligible for best interest rates and fast-track approval."
},
{
"loan_type": "Home Loan",
"risk_category": "Medium Risk",
"required_conditions": (
"credit_score >= 680",
"stable_income >= 2 years",
"debt_to_income_ratio < 40%"
),
"notes": "May require collateral or higher interest rate."
},
{
"loan_type": "Personal Loan",
"risk_category": "Medium Risk",
"required_conditions": (
"credit_score >= 650",
"stable_income >= 2 years"
),
"notes": "Manual verification recommended for income consistency."
},
{
"loan_type": "Auto Loan",
"risk_category": "Low Risk",
"required_conditions": (
"credit_score >= 700",
"stable_income >= 2 years"
),
"notes": "Vehicle acts as secured collateral."
}
)
loan_recommendations = (
{
"risk_category": "Low Risk",
"next_step": "Auto approve loan with standard or best interest rate."
},
{
"risk_category": "Medium Risk",
"next_step": "Approve with adjusted interest rate or require collateral."
},
{
"risk_category": "High Risk",
"next_step": "Reject or request guarantor and additional documents."
}
)
applicant_records = (
{
"applicant_id": "A101",
"age": 30,
"employment_type": "Salaried",
"annual_income": 1200000,
"credit_score": 780,
"debt_to_income_ratio": 25,
"loan_type": "Home Loan",
"requested_amount": 4500000,
"notes": "Working in MNC for 5 years. No missed EMI history."
},
{
"applicant_id": "A102",
"age": 42,
"employment_type": "Self Employed",
"annual_income": 900000,
"credit_score": 690,
"debt_to_income_ratio": 38,
"loan_type": "Home Loan",
"requested_amount": 3500000,
"notes": "Business income fluctuates but stable last 2 years."
},
{
"applicant_id": "A103",
"age": 27,
"employment_type": "Salaried",
"annual_income": 600000,
"credit_score": 640,
"debt_to_income_ratio": 45,
"loan_type": "Personal Loan",
"requested_amount": 500000,
"notes": "Recent job change. Credit card utilization high."
}
)الخطوة 5: بناء الأدوات اللازمة لوكلائنا
يحتاج كل وكيل إلى أجهزة للتواصل مع بياناتنا. إنها وظائف بايثون بسيطة مزينة بأداة زخرفة بايثون؛ والتي يتم استدعاؤها بواسطة LLM عندما يُطلب منك القيام بأشياء معينة.
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-4.1-mini",
temperature=0.0,
timeout=None
)
@tool
def fetch_applicant_record(applicant_id: str) -> dict:
"""
Fetches and summarizes an applicant financial record based on the given applicant ID.
Returns a human-readable summary including income, credit score, loan type,
debt ratio, and financial notes.
Args:
applicant_id (str): The unique identifier for the applicant.
Returns:
dict: {
"applicant_summary": str
}
"""
for record in applicant_records:
if record("applicant_id") == applicant_id:
summary = (
"Here is the applicant financial summary report:\n"
f"Applicant ID: {record('applicant_id')}\n"
f"Age: {record('age')}\n"
f"Employment Type: {record('employment_type')}\n"
f"Annual Income: {record('annual_income')}\n"
f"Credit Score: {record('credit_score')}\n"
f"Debt-to-Income Ratio: {record('debt_to_income_ratio')}\n"
f"Loan Type Requested: {record('loan_type')}\n"
f"Requested Amount: {record('requested_amount')}\n"
f"Financial Notes: {record('notes')}"
)
return {"applicant_summary": summary}
return {"error": "Applicant record not found."}
@tool
def match_risk_policy(loan_type: str, risk_category: str) -> dict:
"""
Match a given loan type and risk category to the most relevant risk policy rule.
Args:
loan_type (str): The loan product being requested.
risk_category (str): The evaluated applicant risk category.
Returns:
dict: A summary of the best matching policy if found, or a message indicating no match.
"""
context = "\n".join((
f"{i+1}. Loan Type: {p('loan_type')}, Risk Category: {p('risk_category')}, "
f"Required Conditions: {p('required_conditions')}, Notes: {p('notes')}"
for i, p in enumerate(risk_policies)
))
prompt = f"""You are a financial risk reviewer assessing whether a loan request aligns with existing lending risk policies.
Instructions:
- Analyze the loan type and applicant risk category.
- Compare against the list of provided risk policy rules.
- Select the policy that best fits the case considering loan type and risk level.
- If none match, respond: "No appropriate risk policy found for this case."
- If a match is found, summarize the matching policy clearly including any required financial conditions or caveats.
Loan Case:
- Loan Type: {loan_type}
- Risk Category: {risk_category}
Available Risk Policies:
{context}
"""
result = llm.invoke(prompt).text
return {"matched_policy": result}
@tool
def check_policy_validity(
financial_indicators: list(str),
required_conditions: list(str),
notes: str
) -> dict:
"""
Determine whether the applicant financial profile satisfies policy eligibility criteria.
Args:
financial_indicators (list(str)): Financial indicators derived from applicant record.
required_conditions (list(str)): Conditions required by matched policy.
notes (str): Additional financial or employment context.
Returns:
dict: A string explaining whether the loan request is financially justified.
"""
prompt = f"""You are validating a loan request based on documented financial indicators and policy criteria.
Instructions:
- Assess whether the applicant financial indicators and notes satisfy the required policy conditions.
- Consider financial context nuances.
- Provide a reasoned judgment if the loan is financially justified.
- If not qualified, explain exactly which criteria are unmet.
Input:
- Applicant Financial Indicators: {financial_indicators}
- Required Policy Conditions: {required_conditions}
- Financial Notes: {notes}
"""
result = llm.invoke(prompt).text
return {"validity_result": result}
@tool
def recommend_loan_action(risk_category: str) -> dict:
"""
Recommend next lending step based on applicant risk category.
Args:
risk_category (str): The evaluated applicant risk level.
Returns:
dict: Lending recommendation string or fallback if no match found.
"""
options = "\n".join((
f"{i+1}. Risk Category: {r('risk_category')}, Recommendation: {r('next_step')}"
for i, r in enumerate(loan_recommendations)
))
prompt = f"""You are a financial lending decision assistant suggesting next steps for a given applicant risk category.
Instructions:
- Analyze the provided risk category.
- Choose the closest match from known lending recommendations.
- Explain why the match is appropriate.
- If no suitable recommendation exists, return: "No lending recommendation found for this risk category."
Risk Category Provided:
{risk_category}
Available Lending Recommendations:
{options}
"""
result = llm.invoke(prompt).text
return {"recommendation": result}
الخطوة 6: تنفيذ الوكلاء الفرعيين (العمال)
نحن الآن نشكل عملاءنا الخاصين الثلاثة. يتم تزويد كل وكيل بموجه نظام ضيق للغاية يشرح له ما يجب عليه فعله والأدوات المسموح له بالوصول إليها، بالإضافة إلى كيفية تنظيم مخرجاته.
case_intake_agent = create_agent(
model=llm,
tools=(fetch_applicant_record),
system_prompt=r"""
You are a Financial Case Intake Specialist.
THIS IS A RULED TASK. FOLLOW THE STEPS IN ORDER. DO NOT SKIP STEPS.
--- MANDATORY EXECUTION RULES ---
- You MUST call the `fetch_applicant_record` tool before writing ANY analysis or summary.
- If you do not have applicant data from the tool, you MUST stop and say: "Applicant data not available."
- Do NOT hallucinate, infer, or invent financial facts beyond what is provided.
- Inference is allowed ONLY when logically derived from financial notes.
--- STEP 1: DATA ACQUISITION (REQUIRED) ---
Call `fetch_applicant_record` and read:
- Financial indicators
- Financial profile / risk context
- Loan request
- Financial notes
You may NOT proceed without this step.
--- STEP 2: FINANCIAL ANALYSIS ---
Using ONLY the retrieved data:
1. Summarize the applicant financial case.
2. Identify explicit financial indicators.
3. Identify inferred financial risks (label as "inferred").
4. Derive rationale for why the loan may have been requested.
--- STEP 3: VALIDATION CHECK ---
Before finalizing, confirm:
- No financial facts were added beyond tool output.
- Inferences are financially reasonable.
- Summary is neutral and review-ready.
--- FINAL OUTPUT FORMAT (STRICT) ---
Sub-Agent Name: Case Intake Agent
Financial Summary:
- ...
Key Financial Indicators:
- Explicit:
- ...
- Inferred:
- ...
Financial Rationale for Loan Request:
- ...
If any section cannot be completed due to missing data, state that explicitly.
"""
)
lending_decision_agent = create_agent(
model=llm,
tools=(recommend_loan_action),
system_prompt=r"""
You are a Lending Decision Recommendation Specialist.
YOU MUST RESPECT PRIOR AGENT DECISIONS.
--- NON-NEGOTIABLE RULES ---
- You MUST read Intake Agent and Risk Policy Checker outputs first.
- You MUST NOT override or contradict the Risk Policy Checker.
- You MUST clearly state whether loan request was:
- Approved
- Not Approved
- Not Validated
--- STEP 1: CONTEXT REVIEW ---
Identify:
- Confirmed financial profile / risk category
- Policy decision outcome
- Key financial risks and constraints
--- STEP 2: DECISION-AWARE PLANNING ---
IF loan request APPROVED:
- Recommend next lending execution steps.
IF loan request NOT APPROVED:
- Do NOT recommend approval.
- Suggest ONLY:
- Additional financial documentation
- Risk mitigation steps
- Financial profile improvement suggestions
- Monitoring or reassessment steps
IF policy NOT FOUND:
- Recommend cautious next steps and documentation improvement.
--- STEP 3: SAFETY CHECK ---
Before finalizing:
- Ensure recommendation does not contradict policy outcome.
- Ensure all suggestions are financially reasonable.
--- FINAL OUTPUT FORMAT (STRICT) ---
Sub-Agent Name: Lending Decision Agent
Policy Status:
- Approved / Not Approved / Not Found
Lending Recommendations:
- ...
Rationale:
- ...
Notes for Reviewer:
- ...
Avoid speculative financial approvals.
Avoid recommending approval if policy validation failed.
"""
)
risk_policy_checker_agent = create_agent(
model=llm,
tools=(match_risk_policy, check_policy_validity),
system_prompt=r"""
You are a Lending Risk Policy Review Specialist.
THIS TASK HAS HARD CONSTRAINTS. FOLLOW THEM EXACTLY.
--- MANDATORY RULES ---
- You MUST base decisions only on:
1. Intake summary content
2. Retrieved risk policy rules
- You MUST NOT approve or reject without a policy check attempt.
- If no policy exists, you MUST explicitly state that.
- Do NOT infer policy eligibility criteria.
--- STEP 1: POLICY IDENTIFICATION (REQUIRED) ---
Use `match_risk_policy` to identify the most relevant policy for:
- The requested loan type
- The evaluated risk category
If no policy is found:
- STOP further validation
- Clearly state that no applicable policy exists
--- STEP 2: CRITERIA EXTRACTION ---
If a policy is found:
- Extract REQUIRED financial conditions exactly as stated
- Do NOT paraphrase eligibility criteria
--- STEP 3: VALIDATION CHECK (REQUIRED) ---
Use `check_policy_validity` with:
- Applicant financial indicators
- Policy required conditions
- Intake financial notes
--- STEP 4: REASONED DECISION ---
Based ONLY on validation result:
- If criteria met → justify approval
- If criteria not met → explain why
- If insufficient data → state insufficiency
--- FINAL OUTPUT FORMAT (STRICT) ---
Sub-Agent Name: Risk Policy Checker Agent
Risk Policy Identified:
- Name:
- Source (if available):
Required Policy Conditions:
- ...
Applicant Evidence:
- ...
Policy Validation Result:
- Met / Not Met / Insufficient Data
Financial Justification:
- ...
Do NOT recommend lending actions here.
Do NOT assume approval unless criteria are met.
"""
)الخطوة 7: العقل المدبر – تنفيذ الوكيل المشرف
هذا هو جوهر نظامنا. دستورها هو موجه المشرف. فهو يحدد الترتيب الصارم لسير العمل وفحوصات الجودة التي يجب إجراؤها على مخرجات كل وكيل قبل المضي قدمًا.
class State(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated(list, add_messages)
members = (
"case_intake_agent",
"risk_policy_checker_agent",
"lending_decision_agent"
)
SUPERVISOR_PROMPT = f"""
You are a Loan Review Supervisor Agent.
You are managing a STRICT, ORDERED loan risk review workflow
between the following agents:
{members}
--- WORKFLOW ORDER (MANDATORY) ---
1. case_intake_agent
2. risk_policy_checker_agent
3. lending_decision_agent
4. FINISH
You MUST follow this order. No agent may be skipped.
--- YOUR RESPONSIBILITIES ---
1. Read all messages so far carefully.
2. Determine which agents have already executed.
3. Inspect the MOST RECENT output of each executed agent.
4. Decide which agent MUST act next based on completeness and order.
--- COMPLETENESS REQUIREMENTS ---
Before moving to the next agent, verify the previous agent’s output contains:
case_intake_agent output MUST include:
- "Financial Summary"
- "Key Financial Indicators"
- "Financial Rationale"
risk_policy_checker_agent output MUST include:
- "Policy Validation Result"
- "Financial Justification"
- Either a policy match OR explicit statement no policy exists
lending_decision_agent output MUST include:
- "Policy Status"
- "Lending Recommendations"
- Clear approval / non-approval status
--- ROUTING RULES ---
- If an agent has NOT run yet → route to that agent.
- If an agent ran but required sections missing → route SAME agent again.
- ONLY return FINISH if all three agents completed correctly.
- NEVER return FINISH early.
--- RESPONSE FORMAT ---
Return ONLY one of:
{members + ("FINISH")}
"""
FINAL_RESPONSE_PROMPT = """
You are the Loan Review Supervisor Agent.
Analyze ALL prior agent outputs carefully.
--- CRITICAL DECISION RULE ---
Your Final Decision MUST be based PURELY on the output of the
lending_decision_agent.
- If lending_decision_agent indicates loan APPROVED
→ Final Decision = APPROVED
- If lending_decision_agent indicates NOT APPROVED or NEEDS INFO
→ Final Decision = NEEDS REVIEW
--- OUTPUT FORMAT (STRICT) ---
- Agent Name: Loan Review Supervisor Agent
- Final Decision: APPROVED or NEEDS REVIEW
- Decision Reasoning: Based on lending_decision_agent output
- Lending recommendation or alternative steps: From lending_decision_agent
"""
class Router(TypedDict):
next: Literal(
"case_intake_agent",
"risk_policy_checker_agent",
"lending_decision_agent",
"FINISH"
)
def supervisor_node(state: State) -> Command(
Literal(
"case_intake_agent",
"risk_policy_checker_agent",
"lending_decision_agent",
"__end__"
)
):
messages = (SystemMessage(content=SUPERVISOR_PROMPT)) + state("messages")
response = llm.with_structured_output(Router).invoke(messages)
goto = response("next")
if goto == "FINISH":
goto = END
messages = (SystemMessage(content=FINAL_RESPONSE_PROMPT)) + state("messages")
response = llm.invoke(messages)
return Command(
goto=goto,
update={
"messages": (
AIMessage(
content=response.text,
name="supervisor"
)
),
"next": goto
}
)
return Command(goto=goto, update={"next": goto})الخطوة 8: تحديد وظائف العقدة
هنا سيتم تحديد وظائف العقدة التي ستؤدي دور عقد laggraph.
def case_intake_node(state: State) -> Command(Literal("supervisor")):
result = case_intake_agent.invoke(state)
return Command(
update={
"messages": (
AIMessage(
content=result("messages")(-1).text,
name="case_intake_agent"
)
)
},
goto="supervisor"
)
def risk_policy_checker_node(state: State) -> Command(Literal("supervisor")):
result = risk_policy_checker_agent.invoke(state)
return Command(
update={
"messages": (
AIMessage(
content=result("messages")(-1).text,
name="risk_policy_checker_agent"
)
)
},
goto="supervisor"
)
def lending_decision_node(state: State) -> Command(Literal("supervisor")):
result = lending_decision_agent.invoke(state)
return Command(
update={
"messages": (
AIMessage(
content=result("messages")(-1).text,
name="lending_decision_agent"
)
)
},
goto="supervisor"
)
الخطوة 9: إنشاء وتصور الرسم البياني
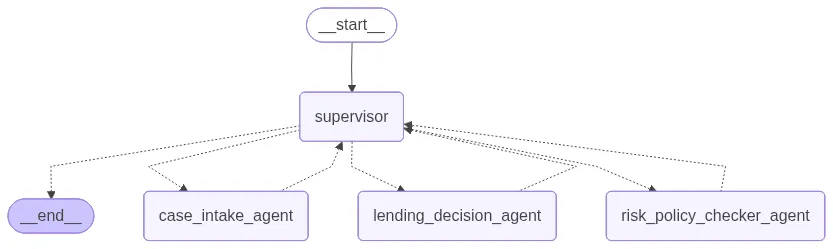
الآن بعد أن حددنا العقد الخاصة بنا، يمكننا إنشاء الرسم البياني لسير العمل. يتم تحديد نقطة الدخول وعقد كل وكيل والحواف الشرطية التي توجه سير العمل حسب قرار المشرف.
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)
graph_builder.add_edge(START, "supervisor")
graph_builder.add_node("supervisor", supervisor_node)
graph_builder.add_node("case_intake_agent", case_intake_node)
graph_builder.add_node("risk_policy_checker_agent", risk_policy_checker_node)
graph_builder.add_node("lending_decision_agent", lending_decision_node)
loan_multi_agent = graph_builder.compile()
loan_multi_agentيمكنك تصور الرسم البياني إذا كان لديك المكتبات المناسبة، ولكننا سنشرع في تشغيله.
الخطوة 10: تشغيل النظام
والآن حانت لحظة الحقيقة. سوف نتقدم كمتقدمين إلى نظامنا ونتبع المشرف لترتيب عملية المراجعة. قبل ذلك، سنقوم بتنزيل وظيفة مساعدة لتنسيق الإخراج.
# This utility file is not essential to the logic but helps format the streaming output nicely.
!gdown 1dSyjcjlFoZpYEqv4P9Oi0-kU2gIoolMB
from agent_utils import format_message
def call_agent_system(agent, prompt, verbose=False):
events = agent.stream(
{"messages": (("user", prompt))},
{"recursion_limit": 25},
stream_mode="values"
)
for event in events:
if verbose:
format_message(event("messages")(-1))
# Display the final response from the agent as Markdown
print("\n\nFinal Response:\n")
if event("messages")(-1).text:
display(Markdown(event("messages")(-1).text))
else:
print(event("messages")(-1).content)
# Return the overall event messages for optional downstream use
return event("messages")
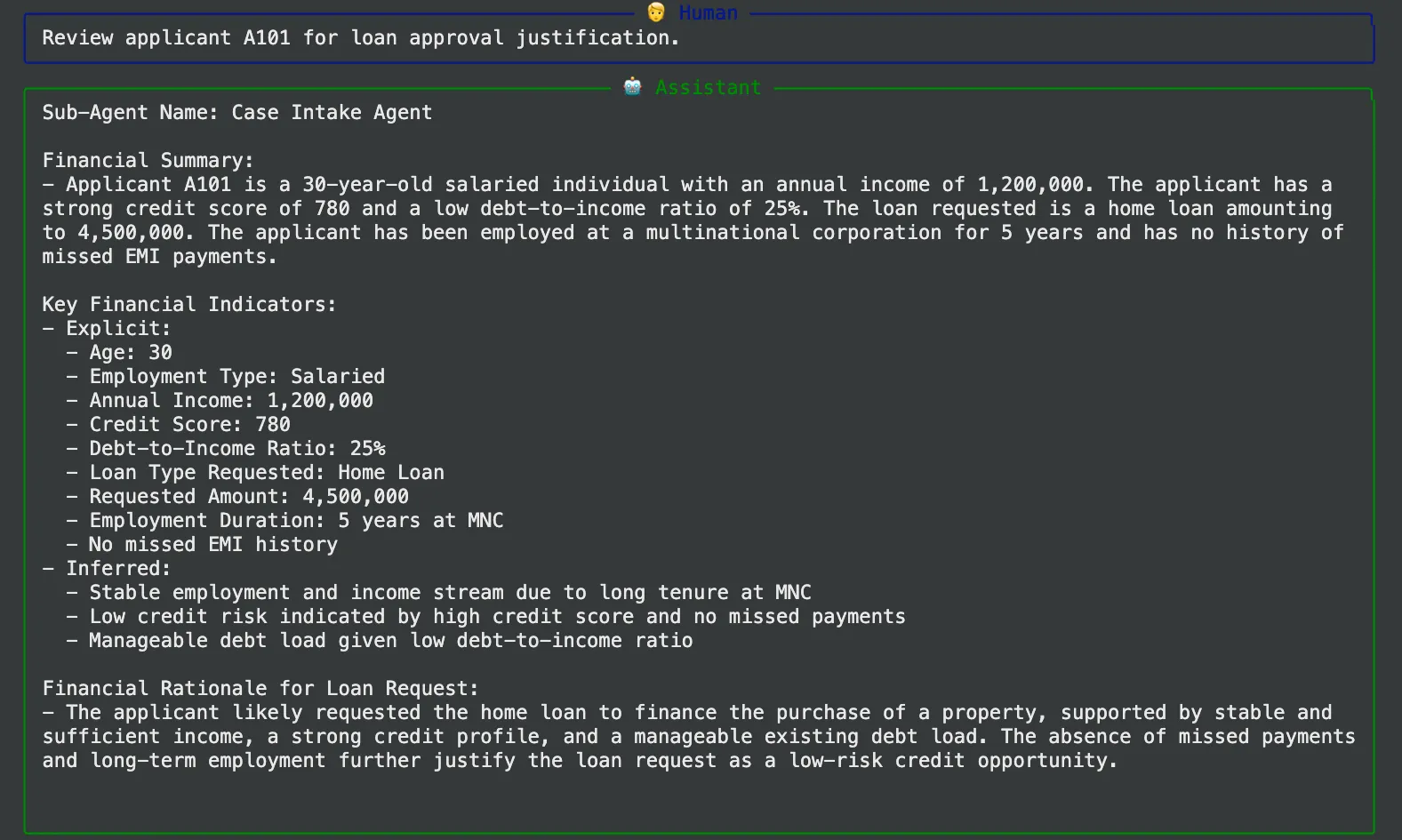
prompt = "Review applicant A101 for loan approval justification."
call_agent_system(loan_multi_agent, prompt, verbose=True)تحليل المخرجات:
عند تشغيل هذا، سترى تتبع التنفيذ خطوة بخطوة:
- المشرف (إلى وكيل معالجة الحالات): يبدأ المشرف العملية بتوجيه المهمة إلى وكيل الاستلام.
- مخرجات عامل تناول العلبة: وهو الوكيل الذي سيقوم بتشغيل أداته لاسترداد سجل مقدم الطلب A101 وإنشاء ملخص مالي نظيف.
- المشرف -> وكيل مدقق سياسة المخاطر: يلاحظ المشرف أنه تم إجراء عملية الاستلام ويقوم بإحالة المهمة إلى مدقق السياسة.
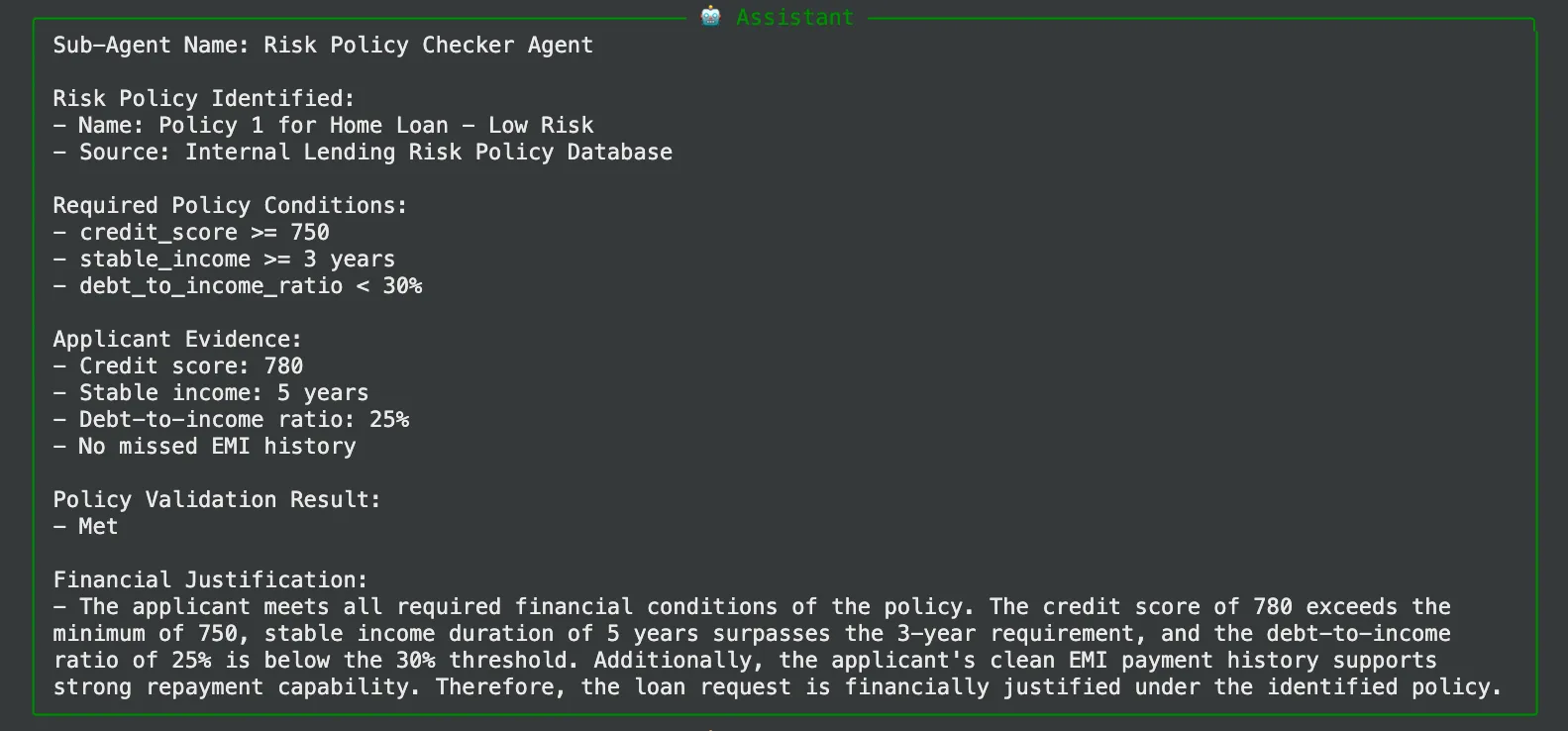
- مخرجات Riskpolicycheckeragent: سيجد وكيل البوليصة أن A101 هي بوليصة منخفضة المخاطر تلبي جميع متطلبات الملف الشخصي الخاصة بقرض السكن.
- المشرف -> وكيل إقراض: يقوم المشرف الآن بتحريض صانع القرار النهائي.
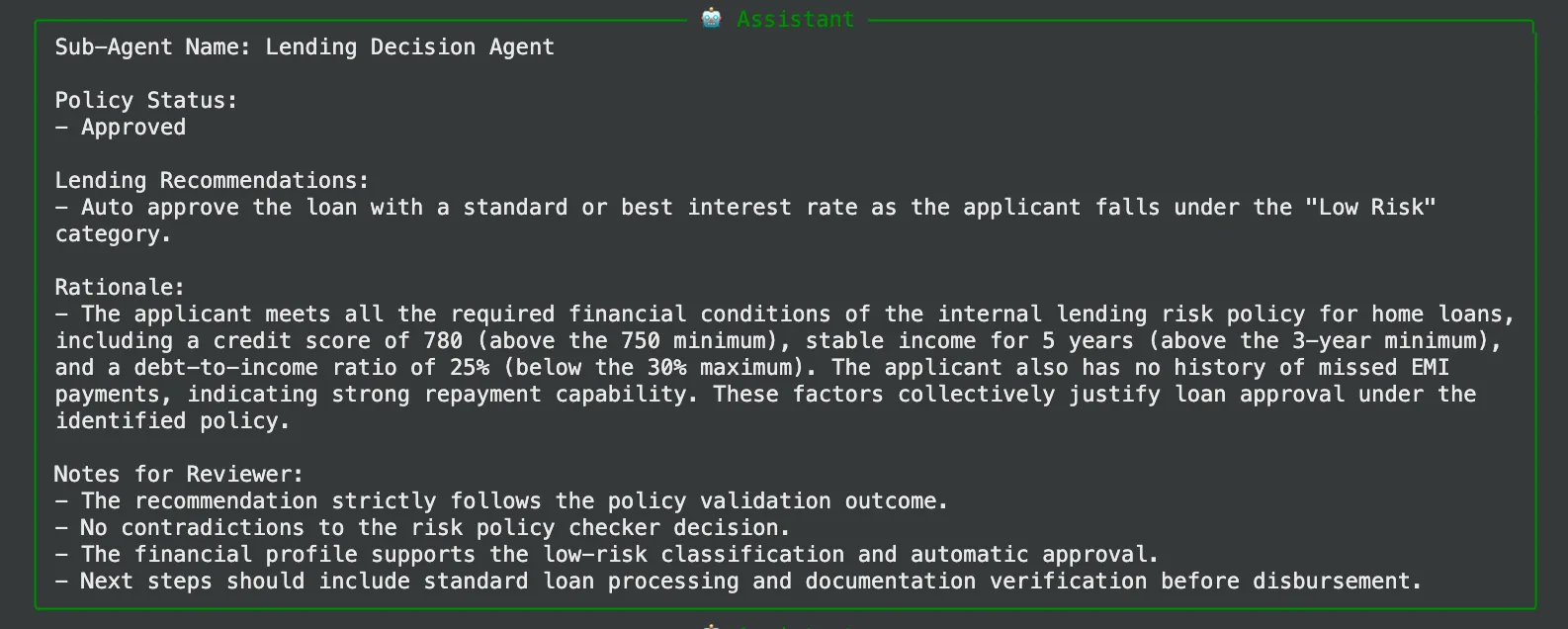
- مخرجات وكيل قرار الإقراض: سيوصي هذا الوكيل بالموافقة التلقائية في فئة “منخفضة المخاطر”.
- المشرف -> إنهاء: عندما يصل المشرف ينهي، فهو يتعامل مع العامل النهائي على أنه مكتمل وينتج ملخصًا تراكميًا.

سيكون المنتج النهائي عبارة عن رسالة مكتوبة بشكل جيد وخالية من أي أوساخ مثل:

دفتر كولاب: إتقان المشرف Agents.ipynb
خاتمة
باستخدام وكيل مشرف، قمنا بتغيير عملية الأعمال المعقدة إلى سير عمل يمكن التنبؤ به وقوي وقابل للتدقيق. فحتى وكيل واحد يحاول التعامل مع استرجاع البيانات، وتحليل المخاطر، واتخاذ القرار في وقت واحد، سيحتاج إلى مطالبة أكثر تعقيدًا بكثير، ومن المرجح أن يرتكب خطأً.
يقدم نمط المشرف نموذجًا عقليًا قويًا ونهجًا معماريًا لتطوير أنظمة الذكاء الاصطناعي المتقدمة. فهو يمكّنك من تفكيك التعقيد وتعيين مسؤولية متميزة وإنشاء سير عمل ذكي وآلي يشبه فعالية فريق بشري جيد التنسيق. الطريقة الثانية لمواجهة التحدي الموحد لا تتمثل في مجرد إنشاء وكيل في المرة القادمة، بل فريقًا، ويكون له مشرف دائمًا.
الأسئلة المتداولة
أ. الموثوقية والنمطية هي القوة الأساسية. يصبح بناء النظام بأكمله وتصحيح أخطائه وصيانته أسهل لأنه يقسم المهمة المعقدة إلى خطوات أصغر يتعامل معها وكلاء متخصصون، مما يؤدي إلى نتائج أكثر اتساقًا وقابلية للتنبؤ بها.
أ. نعم. في هذا الإعداد، يقوم المشرف بإعادة تعيين مهمة إلى نفس الوكيل عندما تكون مخرجاتها غير مكتملة. يمكن للمشرفين الأكثر تقدمًا المضي قدمًا عن طريق إضافة منطق تصحيح الأخطاء أو طلب رأي ثانٍ من وكيل آخر.
ج: على الرغم من أنه يتألق في عمليات سير العمل المعقدة، إلا أن هذا النمط يتعامل أيضًا مع المهام المعقدة إلى حد ما من خلال خطوتين أو ثلاث خطوات فقط. إنه يطبق ترتيبًا منطقيًا ويجعل عملية التفكير الخاصة بالذكاء الاصطناعي أكثر شفافية وقابلية للتدقيق بشكل ملحوظ.
قم بتسجيل الدخول لمواصلة القراءة والاستمتاع بالمحتوى الذي ينظمه الخبراء.
Source link